Partition Recovery Concepts
For a machine to be able to start booting properly, the following conditions must be met:
- Master Boot Record (referred to as the MBR) exists and is safe
- Partition Table exists and contains at least one active partition
If so, executable code in the MBR passes control to an active partition, allowing it to load proper files (for example COMMAND.COM, NTLDR, etc...) depending on the file system type on that partition. If these files are missing or corrupted then the Operating System (referred to as the OS) will be unbootable. Remember the famous error "NTLDR is missing ..." ?
In this case, recovery software can access this drive on the low level, bypassing the system boot (for example, booting from another HDD or bootable floppy) and help you to see all of the other files and directories on the drive . This allows you to copy them to a safe place on another drive.
For the partition/drive to be visible to the OS, the following conditions must be met:
- Partition/Drive can be found via Partition Table
- Partition/Drive boot sector is safe
If so, the OS can read the partition/drive parameters and display the drive in the list of available drives. If the file system itself (i.e. the Root, FAT area on FAT12/FAT16/FAT32, or system MFT records on NTFS) is damaged, the drive's contents may not be displayed and we might see errors like "MFT is corrupted", "Drive is invalid", etc... You are less likely to restore your data in this case, compared to the case where the OS is not bootable due to the missing or corrupted system files. Recovery software can, however, use tricks to display some (but perhaps not all) of the entries that are still safe and allow you to save your data to another location.
Under "Partition recovery" we mean two things:
-
Physical partition recovery. The goal is to find the problem and correct it on the HDD, allowing the partition to be visible to OS again. You can do this manually using Disk Editors or use recovery software designed for this purpose.
-
Virtual partition recovery. The goal is to determine the critical parameters of the deleted/damaged/overwritten partition and display its’ contents. This approach can be applied in some cases when physical partition recovery is not possible (for example, when the partition boot sector is dead) and is commonly used by recovery software. It's very difficult (almost impossible) to implement virtual partition recovery manually.
In the following articles we consider the some topics, related to the recovery of partitions in common general, not specific to the particular file system. We have the following cases:
- MBR is damaged
- Partition is deleted or Partition Table is damaged
- Partition Boot Sector is damaged
- Missing or Corrupted System Files
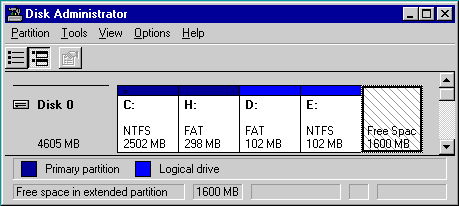
In our examples we'll use the following disk layout:
Recover partitions and disks
Restores lost partitions and disks back to working state
QuickScan for fast partition recovery
QuickScan easily detects partitions which are deleted but not re-formatted
SuperScan for low-level partition detection
SuperScan uses low-level scan process to detect re-formatted and damaged partitions
Last Chance recovery method
Last Chance technology helps with severely damaged filesystems on volumes

